Exploring the Drawbacks of Fossil Fuels

Introduction
Fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, have played a significant role in powering societies across the globe for centuries. However, as we continue to rely heavily on these non-renewable sources of energy, it becomes crucial to understand the numerous drawbacks associated with their use. In this article, we delve into the environmental, health, and economic concerns that arise from our dependence on fossil fuels.
The Environmental Impact
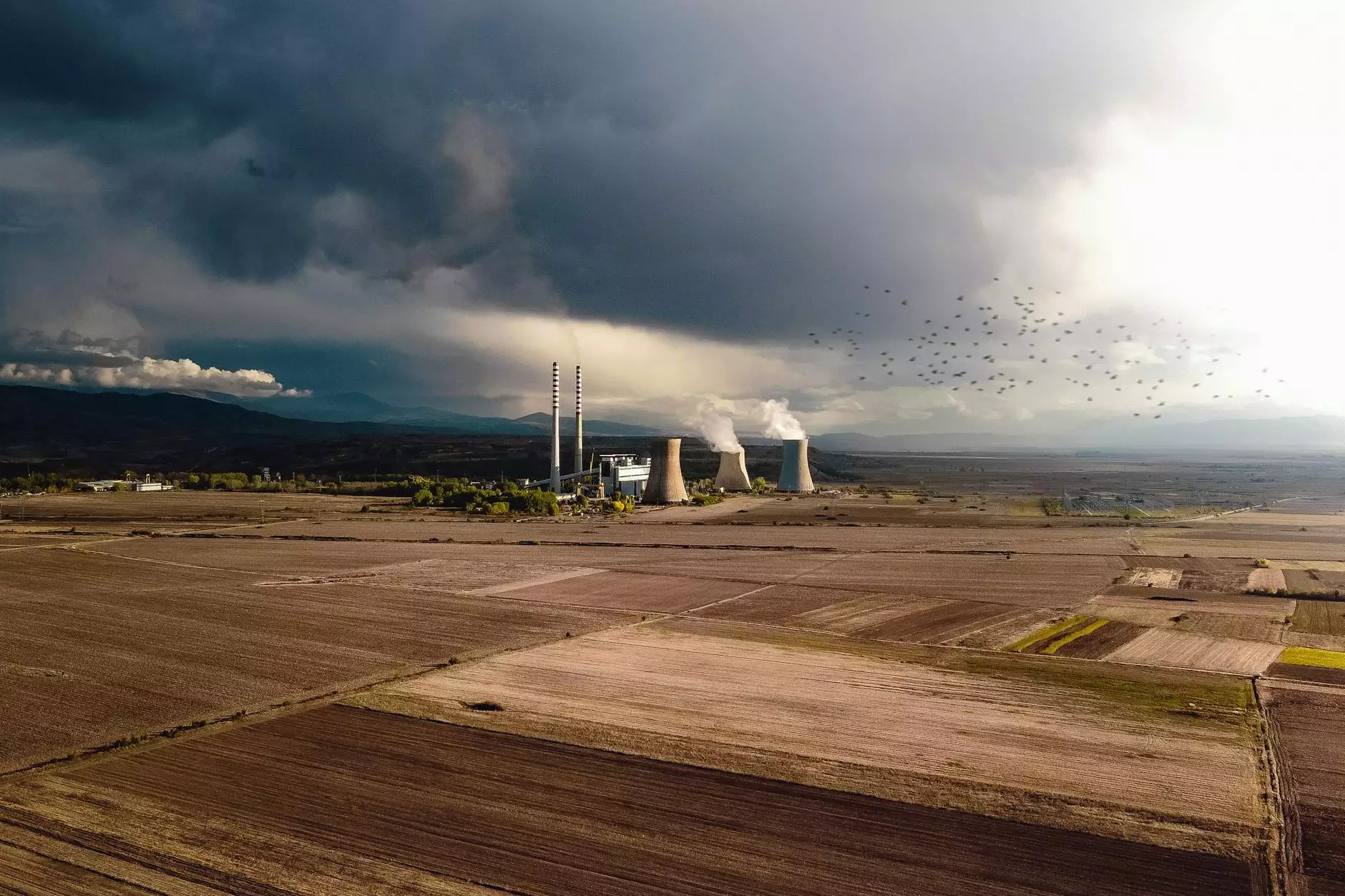
Fossil fuels release large quantities of greenhouse gases, primarily carbon dioxide, into the atmosphere when burned for energy production. This leads to the phenomenon known as global warming, causing climate change and detrimental effects on our planet. Rising sea levels, accelerated melting of polar ice caps, increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, and disrupted ecosystems are just a few examples of the consequences we face due to the excessive carbon emissions.
Air Pollution and Respiratory Health
Aside from contributing to climate change, the burning of fossil fuels also releases harmful pollutants into the air. These pollutants, including sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter, result in air pollution, which has severe implications for respiratory health. Long-term exposure to polluted air can lead to respiratory issues, such as asthma, bronchitis, and other chronic diseases. Furthermore, the emissions from fossil fuel-powered vehicles significantly contribute to urban air pollution, especially in densely populated areas.
Water and Soil Contamination
The extraction and refining processes associated with fossil fuel production can lead to water and soil contamination. Accidental spills during transportation, drilling operations, and leaks from storage tanks can release oil or other pollutants into water bodies, leading to devastating consequences for aquatic ecosystems and wildlife. Additionally, the release of toxic chemicals and heavy metals from mining activities can contaminate soil, rendering it unsuitable for agriculture and harming biodiversity in affected regions.
The Health Implications
Aside from the direct impact on respiratory health from air pollution, the use of fossil fuels has broader health implications for both humans and wildlife. The emissions from power plants and industrial facilities contribute to the formation of smog, which poses a significant risk to respiratory health and can worsen existing medical conditions. Additionally, exposure to pollutants emitted from fossil fuel combustion has been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, neurological disorders, and even certain types of cancer.
The Economic Concerns
While fossil fuels have historically been a driving force behind economic growth and development, it is vital to recognize the long-term economic drawbacks associated with their use. The fluctuating prices of fossil fuels can lead to economic uncertainty, as nations that heavily rely on imports may face escalating energy costs. Additionally, the finite nature of fossil fuel reserves means that as they become scarcer, the extraction becomes more challenging and expensive. This can have significant economic implications in terms of energy security and national financial stability.
The Need for Alternative Energy Sources
To mitigate the drawbacks of fossil fuels, there is a growing need for the development and adoption of alternative energy sources. Renewable energy technologies, such as solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal, offer cleaner and more sustainable alternatives to fossil fuels. They produce little to no greenhouse gas emissions during operation, mitigate air pollution, and have a minimal impact on natural resources.
Advantages of Renewable Energy
In addition to their environmental benefits, renewable energy sources can also stimulate economic growth. The renewable energy industry is a major employer, offering job opportunities in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance. The cost of renewable technologies has also been steadily decreasing, making them increasingly competitive with fossil fuels. Moreover, investing in renewable energy infrastructure can enhance energy independence, reduce reliance on imported energy sources, and foster innovation in the clean energy sector.
Conclusion
As we confront the challenges associated with climate change, it becomes imperative to weigh the drawbacks of fossil fuels against the benefits of transitioning to cleaner, more sustainable energy sources. Our continued reliance on fossil fuels poses severe threats to the environment, human health, and the global economy. By embracing renewable energy technologies and adopting sustainable practices, we can significantly reduce our carbon footprint, cultivate a healthier planet, and pave the way for a brighter future for generations to come.